IJMS Free FullText Metabolic Reprogramming in Sickle Cell Diseases
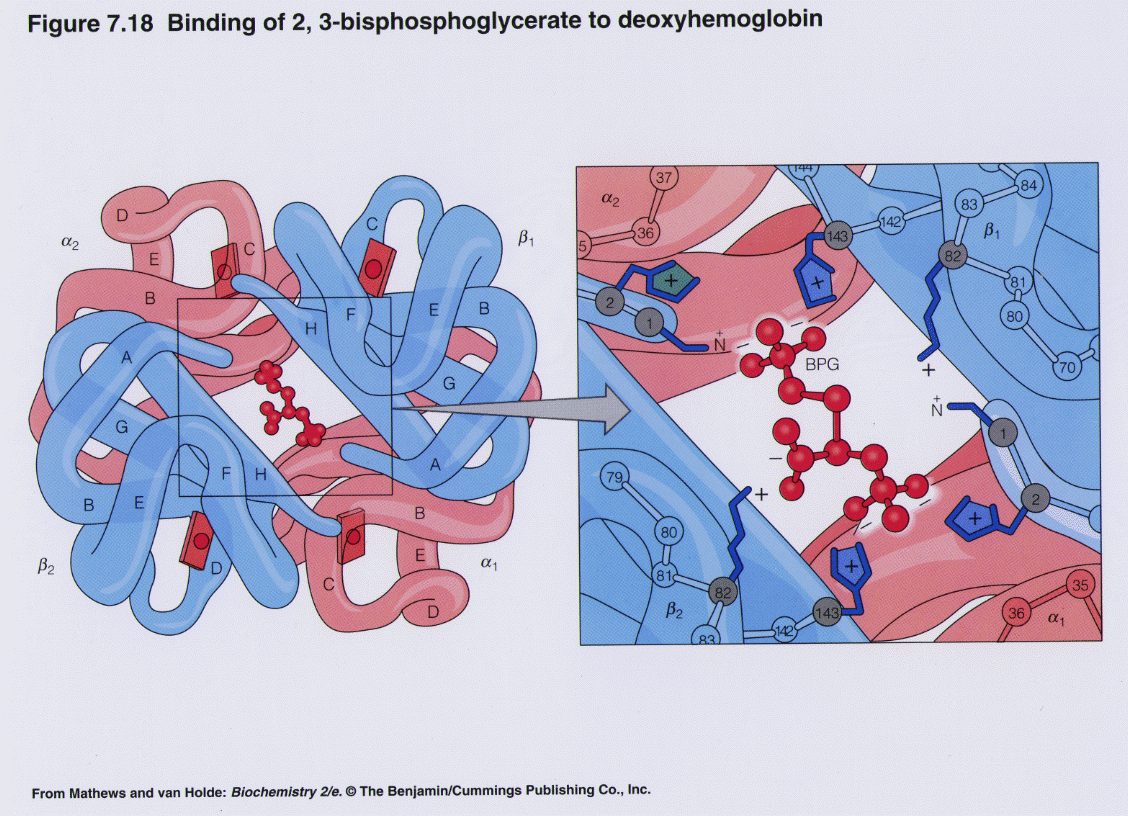
In contrast to the T structure, the ensemble relaxed structures have relatively smaller β-clefts explaining their lower affinity for 2,3-BPG, although liganded R state Hb with the largest β-cleft among the relaxed structures is known to bind 2,3-BPG, albeit at a lower affinity than deoxygenated Hb (Gupta et al. 1979).
Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency Geeky Medics
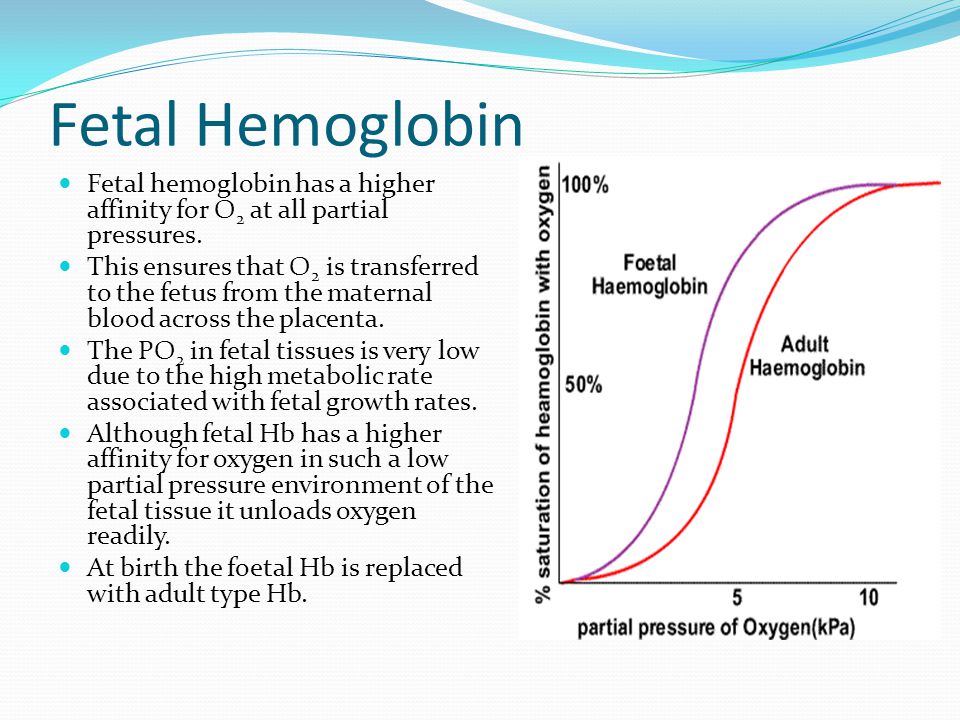
Of an adult's haemoglobin, 2.2-3.5% is HbA 2, composed of two α- and two δ-chains. This form of haemoglobin is poor at oxygen carriage. Fetal haemoglobin (HbF) comprises two α-chains and two γ-chains. At birth, 50-95% of a baby's haemoglobin is HbF, but these levels decline after 6 months as more HbA is produced.
What Is The Difference Between Myoglobin Foetal Haemoglobin And Adult
2,3-BPG both in these patients and in normal volunteers.12 These results prompted a recent open-label phase 2 trial involving patients with either β-thalassemia or α-thalassemia who had

2,3 BPG and Hemoglobin YouTube
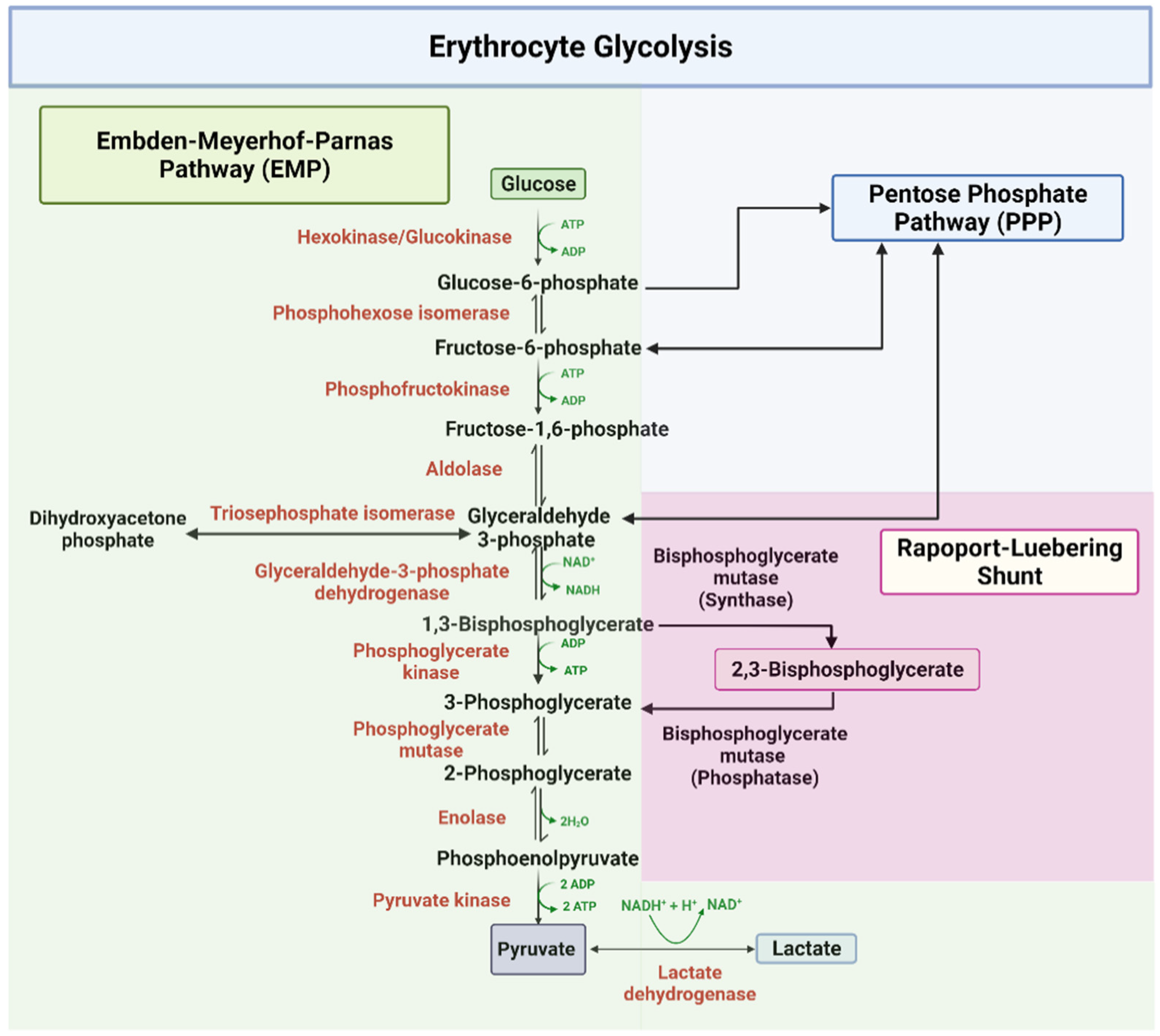
2,3-BPG is formed from 1,3-BPG by the enzyme BPG mutase.It can then be broken down by 2,3-BPG phosphatase to form 3-phosphoglycerate.Its synthesis and breakdown are, therefore, a way around a step of glycolysis, with the net expense of one ATP per molecule of 2,3-BPG generated as the high-energy carboxylic acid-phosphate mixed anhydride bond is cleaved by bisphosphoglycerate mutase.
2,3BPG Binding by Hemoglobin
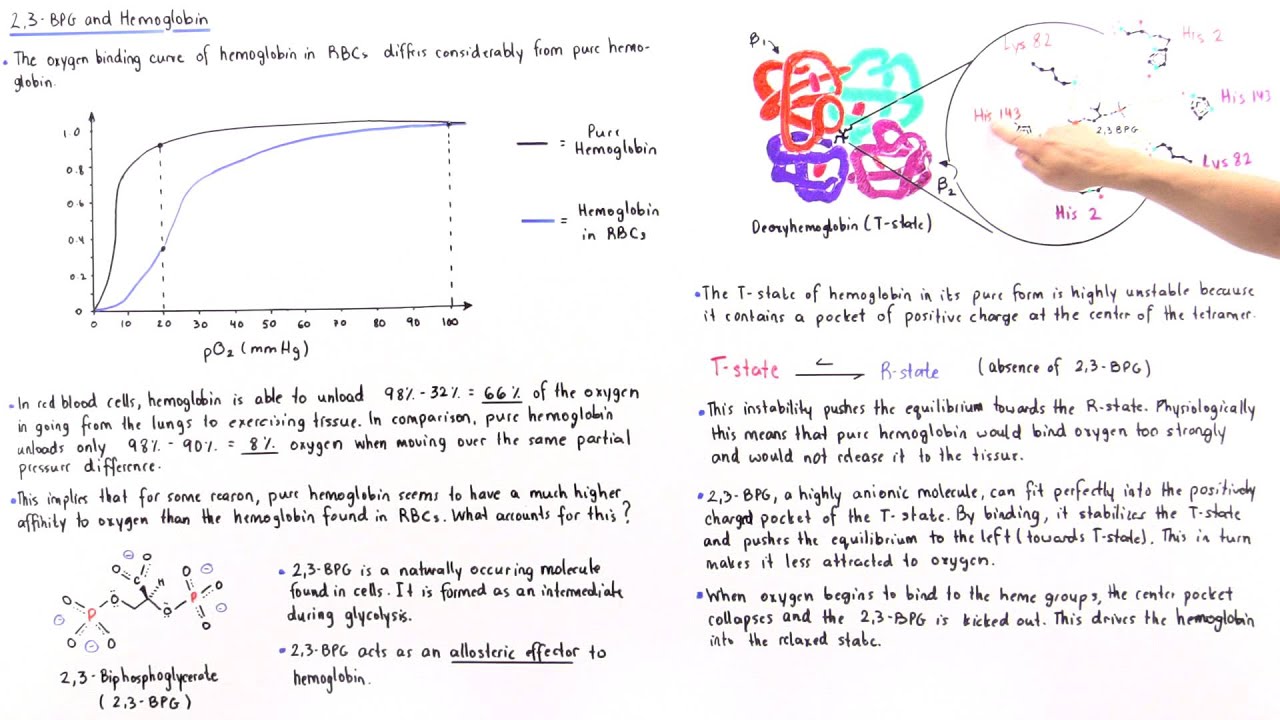
Regulation of the unloading of oxygen from the red blood cells to the target tissues is mainly by the concentration of 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG) within erythrocytes. 2,3-BPG preferentially binds to and stabilizes the deoxygenated form of hemoglobin, resulting in a lower affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen at a given oxygen tension and a subsequent increase in the availability of free.

Synergetic effects of phthalide derivatives and 2,3BPG in modulating
2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) concentrations: BPG is a molecule in red blood cells that binds to hemoglobin and decreases its oxygen affinity. Higher levels of BPG are generally found in situations with low oxygen availability (e.g., at high altitudes or in chronic lung diseases). HbF naturally has a higher affinity for BPG compared with HbA.

Pin on Metabolic Pathways
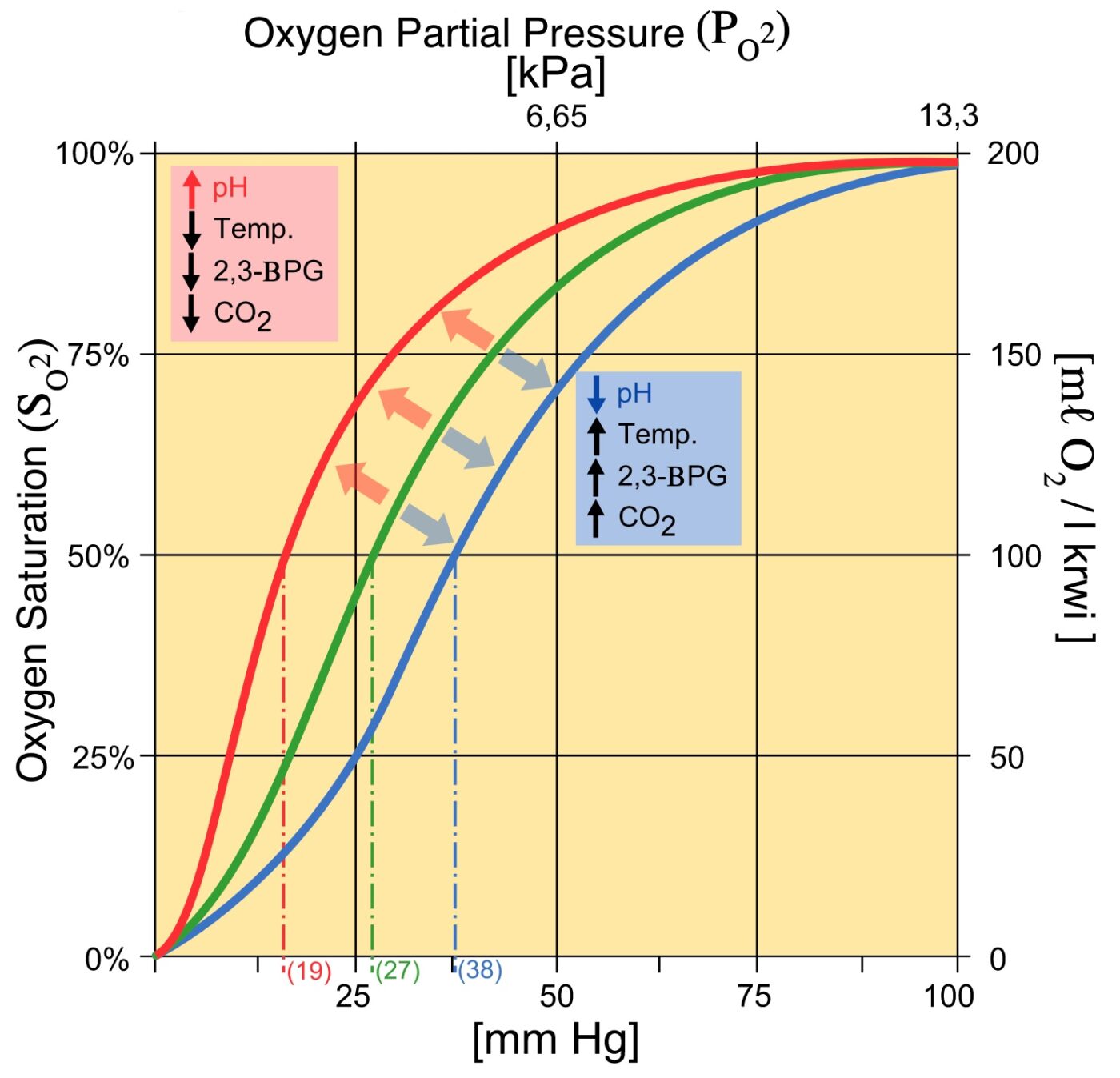
2,3 Diphosphoglycerate (DPG) 2,3-Diphosphoglycerate (DPG) is an intermediate product of glycolysis that is produced within the red blood cell that affects hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen. High concentrations of 2,3-DPG will shift the dissociation curve to the right whereas low concentrations will shift the curve to the left. [1]
PPT Myoglobin & Hemoglobin PowerPoint Presentation, free download
2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate: Human RBCs normally have low levels of 2,3-BPG. During decreased availability of oxygen, as in high altitudes, respiratory diseases such as asthma, or chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD), there is an increase in the conversion of the glycolytic intermediate 1,3-BPG to 2,3-BPG by the action of bisphosphoglycerate mutase. 2,3-BPG binds to deoxyhemoglobin with.

Hypoxiainduced alterations in measured concentrations of ATP and
As a result, the red-cell 2,3-BPG level was elevated by a factor of 2.5, which is considerably higher than the level in most other patients with anemia, with a marked shift to the right in the.

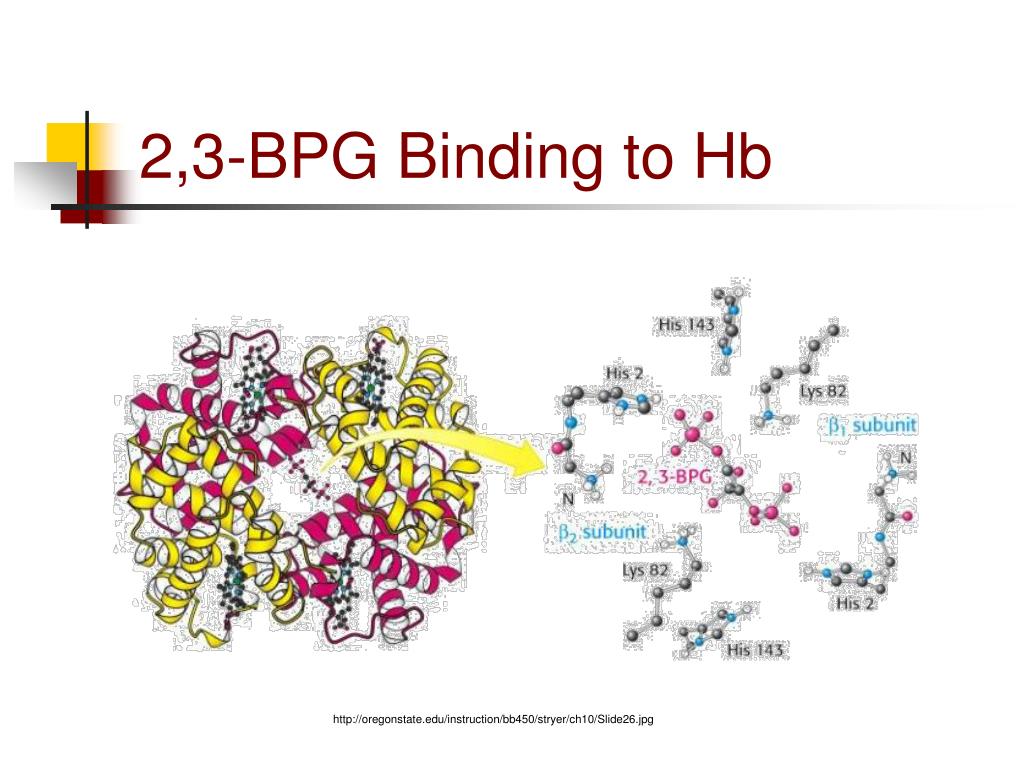
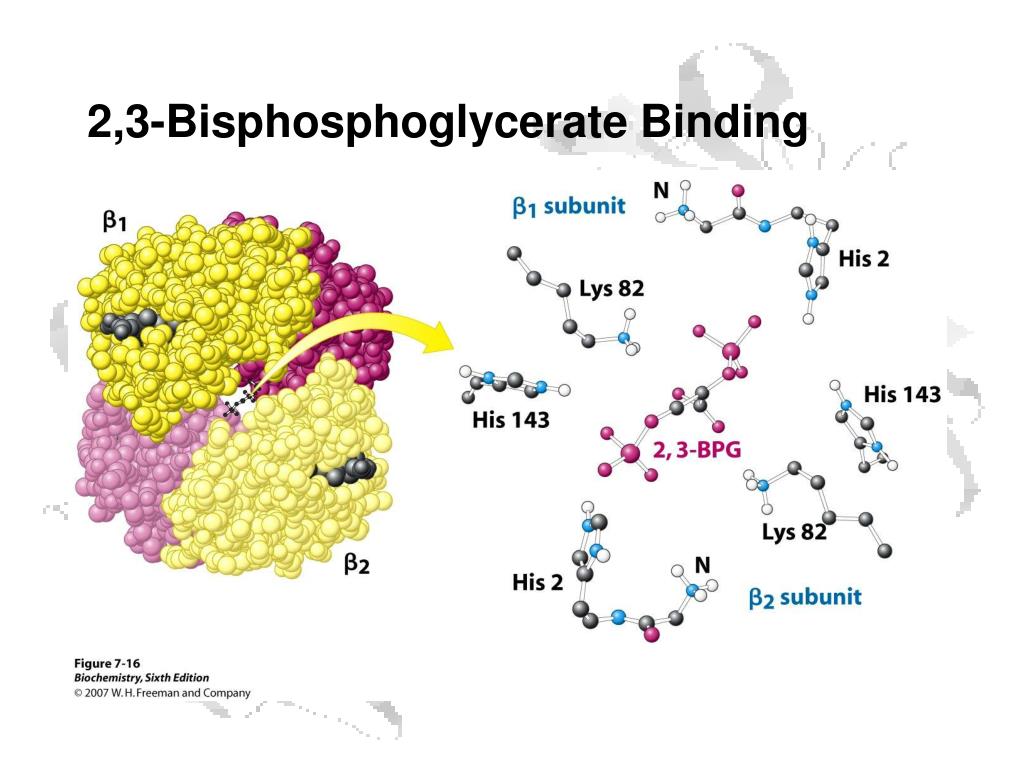
Solved 을 mediaweb.fíu.edu Thought Question 8 Lys82 His2
2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG; 2,3-diphosphoglycerate) is a highly anionic compound that is concentrated in the concave center of red blood cells and binds to hemoglobin, which makes it possible to transport carbon dioxide in deoxyhemoglobin and stabilizes the union, causing oxygen to become reduced.
PPT Protein Function Oxygen Binding Proteins PowerPoint Presentation
(2) The binding of 2,3-BPG to haemoglobin lowers the affinity of the haemoglobin for oxygen. (3) Binding of 2,3-BPG to haemoglobin reduces the Bohr effect. (4) When 2,3-BPG is absent, oxy-haemoglobin is less likely to unload oxygen. The 'correct' answer was given as (2), but the poster thought that (4) was also correct.
The variable manifestations of disease in pyruvate kinase deficiency
One BPG molecule binds reversibly to a tetramer with the monomers all in the T-form; it stabilizes the T-form, shifting the T⇌R equilibrium toward the T-form (see Fig. 3-10). 2,3-BPG has little effect on the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin at high P o 2 but promotes release of O 2 from hemoglobin at low P o 2. It is formed in the RBC from the glycolytic intermediate, 1,3-BPG, by.

Regulation of glycolytic enzymes by posttranslational modifications
Despite the importance of carefully regulating 2,3-BPG turnover, little is known about how this might be achieved. Some attention has focused on the observation that physiologically relevant alkalinization of erythrocytes increases levels of 2,3-BPG, but the mechanism behind this effect is not clearly established, despite nearly four decades of research into erythrocyte cell biology ().

SOLVED 2,3Bisphosphoglycerate (2,3BPG) is an allosteric modifier
Therefore, deficiency of 2,3-BPG moves the oxygen dissociation curve to the left, less oxygen is delivered to tissues, and a compensatory erythrocytosis results. In the glycolytic pathway, the production of 2,3-BPG involves the conversion of 1,3-BPG to 2,3-BPG catalyzed by bisphosphoglycerate mutase (BPGM).
Effect of 2,3BPG on Hemoglobin YouTube
Especially important for oxygen binding are 2,3-BPG, ATP, Cl −, lactate (La-), and GSH. GSH showed no significant differences between patients with COVID-19 and the "controls." [2,3-BPG] and [La-], however, were increased. Messner et al. have shown that changes in blood composition depend on disease severity.

BPGM deletion diminishes cellular 2,3BPG and PGAM1 phosphorylation a
2,3-diphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG) - 2,3-DPG (sometimes referred to as 2,3-BPG) is a chemical found in red blood cells. It is a product from the glucose metabolic pathway. 2,3-DPG binds to the beta chains of haemoglobin, so increased 2,3-DPG levels results in it binding to haemoglobin, decreasing the affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen.